Introduction
In recent years, loader malware has emerged as a significant threat for organizations worldwide. This trend is expected to continue given the widespread availability of many loader strains within the Malware-as-a-Service (MaaS) marketplace. The MaaS marketplace contains a wide variety of innovative strains which are both affordable, with toolkits ranging from USD 400 to USD 1,650 [1], and continuously improving, aiming to avoid traditional detection mechanisms.
SmokeLoader is one such example of a MaaS strain that has been observed in the wild since 2011 and continues to pose a significant threat to organizations and their security teams.
SmokeLoader’s ability to drop an array of different malware strains onto infected systems, from backdoors, ransomware, cryptominers, password stealers, point-of-sale malware and banking trojans, means its a highly versatile loader that has remained consistently popular among threat actors.
In addition to its versatility, it also exhibits advanced evasion strategies that make it difficult for traditional security solutions to detect and remove, and it is easily distributed via methods like spam emails or malicious file downloads.
Between July and August 2023, Darktrace observed an increasing trend in SmokeLoader compromises across its customer base. The anomaly-based threat detection capabilities of Darktrace DETECT™, coupled with the autonomous response technology of Darktrace RESPOND™, identified and contained the SmokeLoader infections in their initial stages, preventing attackers from causing further disruption by deploying other malicious software or ransomware.
SmokeLoader Details
PROPagate Injection Technique
SmokeLoader utilizes the PROPagate code injection technique, a less common method that inserts malicious code into existing processes in order to appear legitimate and bypass traditional signature-based security measures [2] [3]. In the case of SmokeLoader, this technique exploits the Windows SetWindowsSubclass function, which is typically used to add or change the behavior of Windows Operation System. By manipulating this function, SmokeLoader can inject its code into other running processes, such as the Internet Explorer. This not only helps to disguise the malware's activity but also allows attackers to leverage the permissions and capabilities of the infected process.
Obfuscation Methods
SmokeLoader is known to employ several obfuscation techniques to evade the detection and analysis of security teams. The techniques include scrambling portable executable files, encrypting its malicious code, obfuscating API functions and packing, and are intended to make the malware’s code appear harmless or unremarkable to antivirus software. This allows attackers to slip past defenses and execute their malicious activities while remaining undetected.
Infection Vector and Communication
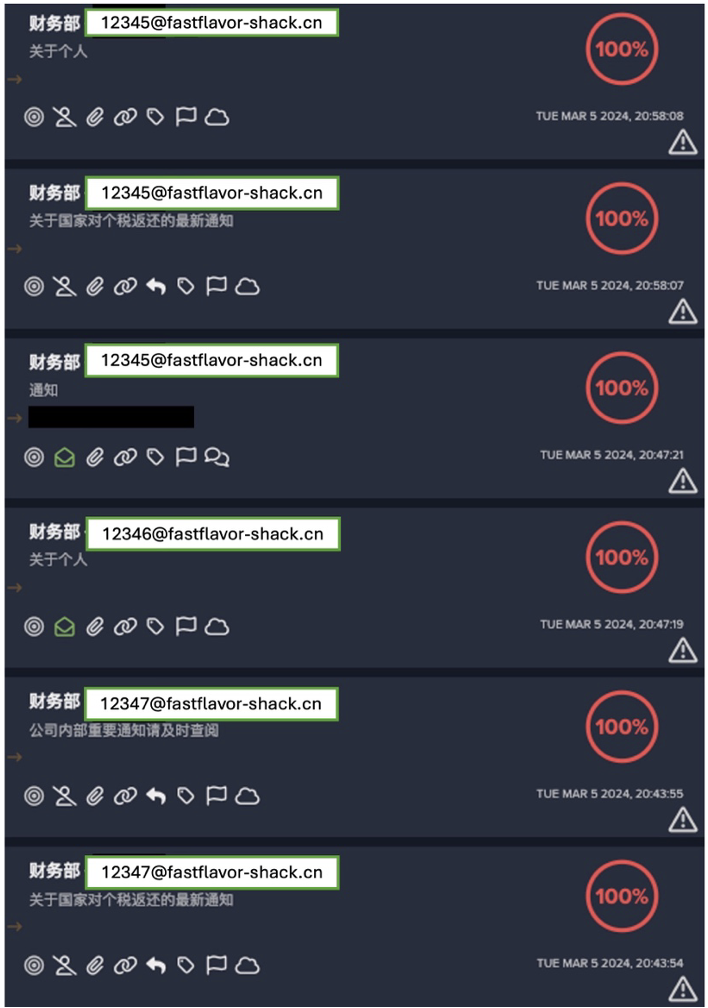
SmokeLoader typically spreads via phishing emails that employ social engineering tactics to convince users to unknowingly download malicious payloads and execute the malware. Once installed on target networks, SmokeLoader acts as a backdoor, allowing attackers to control infected systems and download further malicious payloads from command-and-control (C2) servers. SmokeLoader uses fast flux, a DNS technique utilized by botets whereby IP addresses associated with C2 domains are rapidly changed, making it difficult to trace the source of the attack. This technique also boosts the resilience of attack, as taking down one or two malicious IP addresses will not significantly impact the botnet's operation.
Continuous Evolution
As with many MaaS strains, SmokeLoader is continuously evolving, with its developers regularly adding new features and techniques to increase its effectiveness and evasiveness. This includes new obfuscation methods, injection techniques, and communication protocols. This constant evolution makes SmokeLoader a significant threat and underscores the importance of advanced threat detection and response capabilities solution.
Darktrace’s Coverage of SmokeLoader
Between July and August 2023, Darktrace detected one particular SmokeLoader infection at multiple stages of its kill chain on a customer network. This detection was made possible by Darktrace DETECT’s anomaly-based approach and Self-Learning AI that allows it to identify subtle deviations in device behavior.
One of the key components of this process is the classification of endpoint rarity and determining whether an endpoint is new or unusual for any given network. This classification is applied to various aspects of observed endpoints, such as domains, IP addresses, or hostnames within the network. It thereby plays a vital role in identifying SmokeLoader activity, such as the initial infection vector or C2 communication, which typically involve a device contacting a malicious endpoint associated with SmokeLoader.
The First Signs of Infection SmokeLoader Infection
Beginning in July 2023, Darktrace observed a surge in suspicious activities that were assessed with moderate to high confidence to be associated with SmokeLoader malware.
For example on July 30, a device was observed making a successful HTTPS request to humman[.]art, a domain that had never been seen on the network, and therefore classified as 100% rare by DETECT. During this connection, the device in question received a total of 6.0 KiB of data from the unusual endpoint. Open-source intelligence (OSINT) sources reported with high confidence that this domain was associated with the SmokeLoader C2 botnet.
The device was then detected making an HTTP request to another 100% rare external IP, namely 85.208.139[.]35, using a new user agent. This request contained the URI ‘/DefenUpdate.exe’, suggesting a possible download of an executable (.exe) file. This was corroborated by the total amount of data received in this connection, 4.3 MB. Both the file name and its size suggest that the offending device may have downloaded additional malicious tooling from the SmokeLoader C2 endpoint, such as a trojan or information stealer, as reported on OSINT platforms [4].

The observed new user agent, “Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64; Trident/7.0; rv:11.0) like Gecko” was identified as suspicious by Darktrace leading to the “Anomalous Connection / New User Agent to IP Without Hostname” DETECT model breach.
As this specific user agent was associated with the Internet Explorer browser running on Windows 10, it may not have appeared suspicious to traditional security tools. However, Darktrace’s anomaly-based detection allows it to identify and mitigate emerging threats, even those that utilize sophisticated evasion techniques.
This is particularly noteworthy in this case because, as discussed earlier, SmokeLoader is known to inject its malicious code into legitimate processes, like Internet Explorer.

C2 Communication
Darktrace continued to observe the device making repeated connections to the humman[.]art endpoint. Over the next few days. On August 7, the device was observed making unusual POST requests to the endpoint using port 80, breaching the ‘Anomalous Connection / Multiple HTTP POSTs to Rare Hostname’ DETECT model. These observed POST requests were observed over a period of around 10 days and consisted of a pattern of 8 requests, each with a ten-minute interval.

Upon investigating the details of this activity identified by Darktrace DETECT, a particular pattern was observed in these requests: they used the same user-agent, “Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64; Trident/7.0; rv:11.0) like Gecko”, which was previously detected in the initial breach.
Additionally, they the requests had a constantly changing eferrer header, possibly using randomly generated domain names for each request. Further examination of the packet capture (PCAP) from these requests revealed that the payload in these POST requests contained an RC4 encrypted string, strongly indicating SmokeLoader C2 activity.


Unfortunately in this case, Darktrace RESPOND was not active on the network meaning that the attack was able to progress through its kill chain. Despite this, the timely alerts and detailed incident insights provided by Darktrace DETECT allowed the customer’s security team to begin their remediation process, implementing blocks on their firewall, thus preventing the SmokeLoader malware from continuing its communication with C2 infrastructure.
Darktrace RESPOND Halting Potential Threats from the Initial Stages of Detection
With Darktrace RESPOND, organizations can move beyond threat detection to proactive defense against emerging threats. RESPOND is designed to halt threats as soon as they are identified by DETECT, preventing them from escalating into full-blown compromises. This is achieved through advanced machine learning and Self-Learning AI that is able to understand the normal ‘pattern of life’ of customer networks, allowing for swift and accurate threat detection and response.
One pertinent example was seen on July 6, when Darktrace detected a separate SmokeLoader case on a customer network with RESPOND enabled in autonomous response mode. Darktrace DETECT initially identified a string of anomalous activity associated with the download of suspicious executable files, triggering the ‘Anomalous File / Multiple EXE from Rare External Locations’ model to breach.
The device was observed downloading an executable file (‘6523.exe’ and ‘/g.exe’) via HTTP over port 80. These downloads originated from endpoints that had never been seen within the customer’s environment, namely ‘hugersi[.]com’ and ‘45.66.230[.]164’, both of which had strongly been linked to SmokeLoader by OSINT sources, likely indicating the initial infection stage of the attack [5].
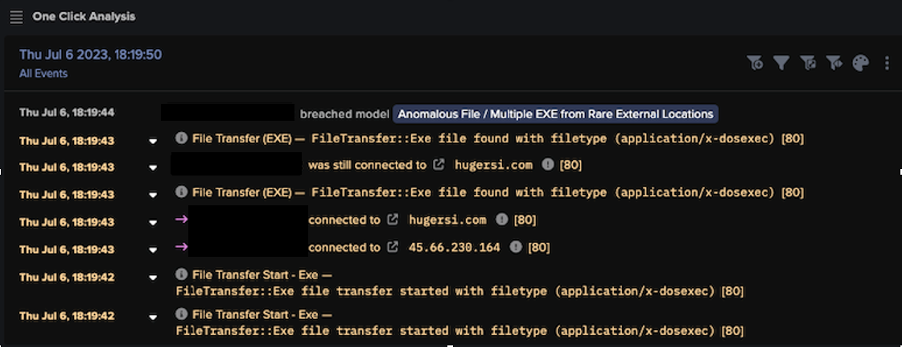
Around the same time, Darktrace also observed the same device downloading an unusual file with a numeric file name. Threat actors often employ this tactic in order to avoid using file name patterns that could easily be recognized and blocked by traditional security measures; by frequently changing file names, malicious executables are more likely to remain undetected.


With Darktrace RESPOND active and enabled in autonomous response mode, the SmokeLoader infection was thwarted in the first instance. RESPOND took swift autonomous action by blocking connections to the suspicious endpoints identified by DETECT, blocking all outgoing traffic, and enforcing a pre-established “pattern of life” on offending devices. By enforcing a patten of life on a device, Darktrace RESPOND ensures that it cannot deviate from its ‘normal’ activity to carry out potentially malicious activity, while allowing the device to continue expected business operations.

In addition to the autonomous mitigative actions taken by RESPOND, this customer also received a Proactive Threat Notification (PTN) informing them of potentially malicious activity on their network. This prompted the Darktrace Security Operations Center (SOC) to investigate and document the incident, allowing the customer’s security team to shift their focus to remediating and removing the threat of SmokeLoader.
Conclusion
Ultimately, Darktrace showcased its ability to detect and contain versatile and evasive strains of loader malware, like SmokeLoader. Despite its adeptness at bypassing conventional security tools by frequently changing its C2 infrastructure, utilizing existing processes to infect malicious code, and obfuscating malicious file and domain names, Darktrace’s anomaly-based approach allowed it to recognize such activity as deviations from expected network behavior, regardless of their apparent legitimacy.
Considering SmokeLoader’s wide array of functions, including C2 communication that could be used to facilitate additional attacks like exfiltration, or even the deployment of information-stealers or ransomware, Darktrace proved to be crucial in safeguarding customer networks. By identifying and mitigating SmokeLoader at the earliest possible stage, Darktrace effectively prevented the compromises from escalating into more damaging and disruptive compromises.
With the threat of loader malware expected to continue growing alongside the boom of the MaaS industry, it is paramount for organizations to adopt proactive security solutions, like Darktrace DETECT+RESPOND, that are able to make intelligent decisions to identify and neutralize sophisticated attacks.
Credit to Patrick Anjos, Senior Cyber Analyst, Justin Torres, Cyber Analyst
Appendices
Darktrace DETECT Model Detections
- Anomalous Connection / New User Agent to IP Without Hostname
- Anomalous Connection / Multiple HTTP POSTs to Rare Hostname
- Anomalous File / Multiple EXE from Rare External Locations
- Anomalous File / Numeric File Download
List of IOCs (IOC / Type / Description + Confidence)
- 85.208.139[.]35 / IP / SmokeLoader C2 Endpoint
- 185.174.137[.]109 / IP / SmokeLoader C2 Endpoint
- 45.66.230[.]164 / IP / SmokeLoader C2 Endpoint
- 91.215.85[.]147 / IP / SmokeLoader C2 Endpoint
- tolilolihul[.]net / Hostname / SmokeLoader C2 Endpoint
- bulimu55t[.]net / Hostname / SmokeLoader C2 Endpoint
- potunulit[.]org / Hostname / SmokeLoader C2 Endpoint
- hugersi[.]com / Hostname / SmokeLoader C2 Endpoint
- human[.]art / Hostname / SmokeLoader C2 Endpoint
- 371b0d5c867c2f33ae270faa14946c77f4b0953 / SHA1 / SmokeLoader Executable
References:
[2] https://malpedia.caad.fkie.fraunhofer.de/details/win.smokeloader
[3] https://www.darkreading.com/cyber-risk/breaking-down-the-propagate-code-injection-attack
[4] https://n1ght-w0lf.github.io/malware%20analysis/smokeloader/
[5] https://therecord.media/surge-in-smokeloader-malware-attacks-targeting-ukrainian-financial-gov-orgs
MITRE ATT&CK Mapping
Model: Anomalous Connection / New User Agent to IP Without Hostname
ID: T1071.001
Sub technique: T1071
Tactic: COMMAND AND CONTROL
Technique Name: Web Protocols
Model: Anomalous Connection / Multiple HTTP POSTs to Rare Hostname
ID: T1185
Sub technique: -
Tactic: COLLECTION
Technique Name: Man in the Browser
ID: T1071.001
Sub technique: T1071
Tactic: COMMAND AND CONTROL
Technique Name: Web Protocols
Model: Anomalous File / Multiple EXE from Rare External Locations
ID: T1189
Sub technique: -
Tactic: INITIAL ACCESS
Technique Name: Drive-by Compromise
ID: T1588.001
Sub technique: - T1588
Tactic: RESOURCE DEVELOPMENT
Technique Name: Malware
Model: Anomalous File / Numeric File Download
ID: T1189
Sub technique: -
Tactic: INITIAL ACCESS
Technique Name: Drive-by Compromise
ID: T1588.001
Sub technique: - T1588
Tactic: RESOURCE DEVELOPMENT
Technique Name: Malware